The capabilities of Soil Mechanics laboratory is mentioned below.

The CBR test is performed by measuring the pressure required to penetrate a soil sample with a plunger of standard area. The measured pressure is then divided by the pressure required to achieve an equal penetration on a standard crushed rock material. The harder the surface, the higher the CBR value.
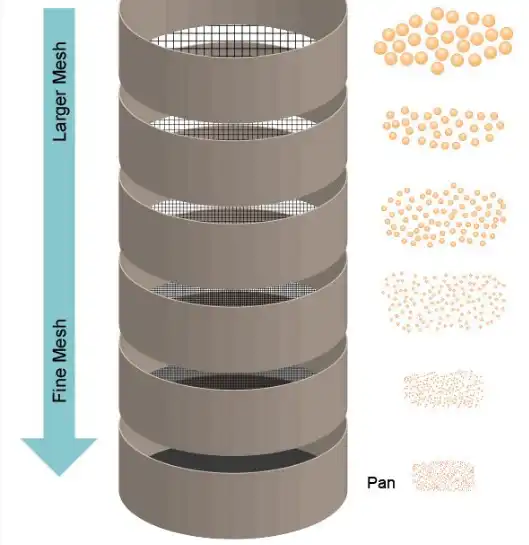
Sieve analysis is a technique used to determine the particle size distribution of a powder. This method is performed by sifting a powder sample through a stack of wire mesh sieves, separating it into discrete size ranges. A sieve shaker is used to vibrate the sieve stack for a specific period of time.
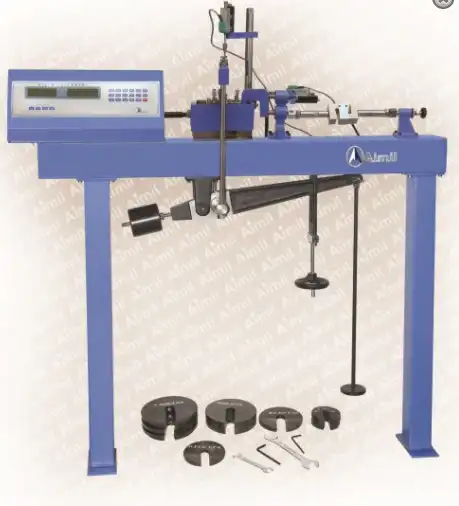

The direct shear test is a laboratory or field test used by geotechnical engineers to measure the shear strength properties of soil or rock material, or of discontinuities in soil or rock masses. The test is standard practice to establish the shear strength properties of discontinuities in rock.

The unconfined compressive strength (qu) is the load per unit area at which the cylindrical specimen of a cohesive soil falls in compression.

The principle of sand replacement method is to measure the in-situ volume of hole from which the material was excavated from the weight of sand with known density filling in the hole. The in-situ density of material is given by the weight of the excavate material divided by the in-situ volume.

Specific gravity of soil grains gives the property of the formation of soil mass and is independent of particle size. It can be determined by pyconometer apparatus.
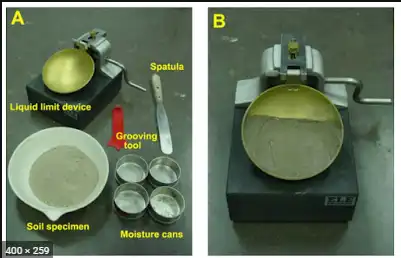
Atterberg limits are a basic measure of the critical water contents of a fine-grained soil: its shrinkage limit, plastic limit, and liquid limit. The boundary between each state can be defined based on a change in the soil's behavior.

The shear vane test is a method of measuring the untrained shear strength of a cohesive soil. A gauge on the top of the rod measures the torque required to cause failure of the soil and provides a conversion to shear strength. The equipment has been in use since at least 1948.

Shrinkage limit of a soil is defined as “the maximum water content at which a reduction in water content will not cause a decrease in volume of the soil mass. The shrinkage ratio is defined as “the ratio of a given volume change, expressed as a per- centage of the dry volume, to the corresponding change in water.
.webp)
A cylindrical core cutter is a seamless steel tube. For determination of the dry density of the soil, the cutter is pressed into the soil mass so that it is filled with the soil. The cutter filled with the soil is lifted up.

Consolidation test is used to determine the rate and magnitude of soil consolidation when the soil is restrained laterally and loaded axially. The Consolidation test is also referred to as Standard Odometer test or One or three dimensional compression test.